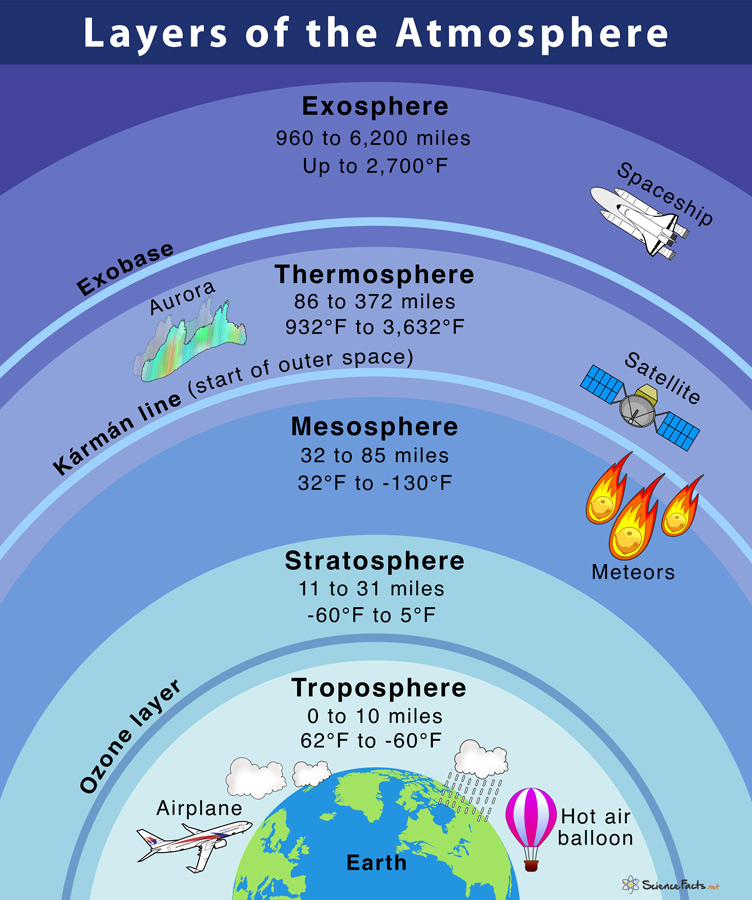
The Exosphere is the upper part of Earth's atmosphere, and has no clear end since it gradually fades into space!
Few molecules reside in this layer and the lighest atmosphere gases hydrogen, and helium exist throughout the exosphere.
The Thermosphere is below the exosphere and makes up the largest measurable layer in Earth's atmosphere.
The thermosphere is very important to life on Earth through its ability to block X-ray and UV raditation from reaching our planet.
When charged particles from the sun react with gaseous particles in the Thermosphere the exciting phenomena of Northern Lights, or Aurora Borealis occurs!
Reflective of its name, the Thermosphere holds an extremely hight temperature, reaching up to 2500 degrees Celcius, way hotter than any other layer!
Another name for this layer is the ionosphere as it traps protons, electrons, and other ions emitted by the sun!
The Mesophere sits below the Thermosphere and above the Stratosphere and gets colder as you get higher within it, which can get to lows of below -115 Fahrenheit.
The Stratosphere houses the Ozone layer and sits above the Troposphere. Due to the Ozone layer absorbing radiation the higher you go in the Stratosphere, the hotter it gets.
Ozone or O3 is integral to human life, as well as the life of all organisms! This layer absorbs UV radiation emitted by the sun and shields the troposphere from detrimental radiation.
The Troposphere begins at the ground and holds the weather and most living organisms.
The higher you go in this layer the colder it gets.